Linux split command: splitting files into slices
Linux split command Function Description
Use the split command to split the input file into pieces and output fixed size blocks, the output file name is "prefix aa", "prefix ab", the default prefix is "x", the default size is 1000 lines.
The split command can split a large file into many smaller files. Sometimes it is necessary to split a file into smaller pieces, for example to improve readability, generate logs, etc.
Linux split command Syntax
split [Option] [Enter [prefix]]The meaning of each option in the command is shown in the following table.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-d |
Use numeric suffixes, not letters |
-C <Size> |
Places the maximum size of lines in each output file in bytes |
-l <Line count> |
Specify how many lines in each output file |
--verbose |
Display diagnostics before each output file is opened |
-a <Suffix length> |
Use a suffix of the specified length, which defaults to 2 |
-b <Size> |
Specifies the size of each output file in bytes |
Linux split command Example
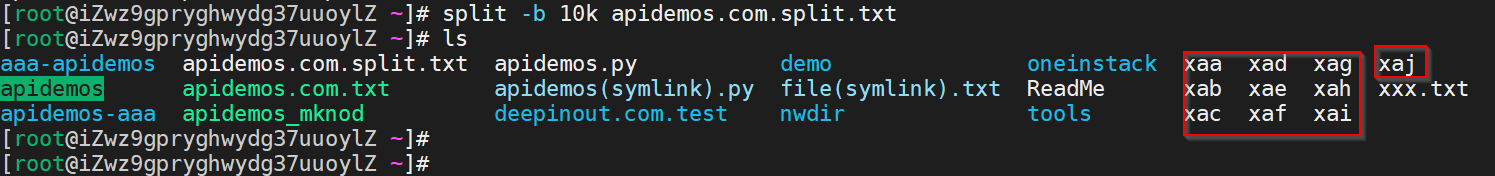
Split the /root/apidemos.com.split.txt file into slices, with each output file having a size of 10k
Split the /root/install.log file into pieces, with each output file being 1024 bytes in size
[root@rhel ~]# split -b 1024 /root/install.logSplit the /root/install.log file into pieces and prefix the output file with PREFIX
[root@rhel ~]# split -b 1024 /root/install.log PREFIXSplit the /root/install.log file into pieces, specifying the number of output file suffixes as 5
[root@rhel ~]# split -a 5 /root/install.logSplit the /root/install.log file into pieces, specifying that each output file has 100 lines
[root@rhel ~]# split -l 100 /root/install.logGenerate a test file with a size of 100KB
[root@localhost split]# dd if=/dev/zero bs=100k count=1 of=date.file
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
102400 bytes (102 kB) copied, 0.00043 seconds, 238 MB/sUse the split command to split the date.file file created above into smaller files of 10KB in size
[root@localhost split]# split -b 10k date.file
[root@localhost split]# ls
date.file xaa xab xac xad xae xaf xag xah xai xajThe file is split into multiple files with alphabetic suffixes, if you want to use numeric suffixes you can use the -d parameter, and you can use -a length to specify the length of the suffix
[root@localhost split]# split -b 10k date.file -d -a 3
[root@localhost split]# ls
date.file x000 x001 x002 x003 x004 x005 x006 x007 x008 x009Specify the file name prefix for the split file
[root@localhost split]# split -b 10k date.file -d -a 3 split_file
[root@localhost split]# ls
date.file split_file000 split_file001 split_file002 split_file003 split_file004 split_file005 split_file006 split_file007 split_file008 split_file009Use the -l option to split the file according to the number of lines in the file
For example, splitting a file into smaller files containing 10 lines each
split -l 10 date.file ApiDemos™
ApiDemos™