Linux mv command: rename files and directories, move files and directory paths.
Linux mv command Function Description
Use the mv command to change the names of files and directories, and to move the paths of files and directories.
The mv command is used to rename files or directories, or to move files from one directory to another. source indicates the source file or directory, and target indicates the target file or directory. If a file is moved to an already existing target file, the contents of the target file will be overwritten.
The mv command can be used to move a source file to a target file, or to move a group of files to a target directory. There are two different results for a source file being moved to a target file.
- If the target file is a path to a directory file, the source file will be moved to this directory and the file name will remain the same.
- If the target file is not a directory file, the source file name (there can be only one) will be changed to this target file name and overwrite the existing file with the same name. If the source file and the target file are in the same directory, the function of mv is to change the file name. When the target file is a directory file, and there can be more than one source file or directory parameter, all the source files will be moved to the target file. All files moved to that directory will keep their previous filenames.
The result of mv and cp is different. mv seems to "move" files, but the number of files does not increase. While cp copies the files, the number of files increases.
Linux mv command Syntax
mv [options] [source file|directory] [target file|directory]The meaning of each option in the command is shown in the table.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-i |
Ask before overwriting |
-f |
Do not ask before overwriting |
-n |
Do not overwrite existing files |
-u |
Move only if the source file is newer than the target file, or if the target file does not exist |
-T |
Treating the target file as a normal file |
Linux mv command Examples
Move all files with the suffix ".png" from the /root/pic directory to the /usr/local/share/pic directory
[root@rhel ~]# mv -f /root/pic/*.png /usr/local/share/picRename the file /root/apidemos.diff.txt to /root/apimodes.mv.txt
mv apidemos.diff.txt apidemos.mv.txtOutput:
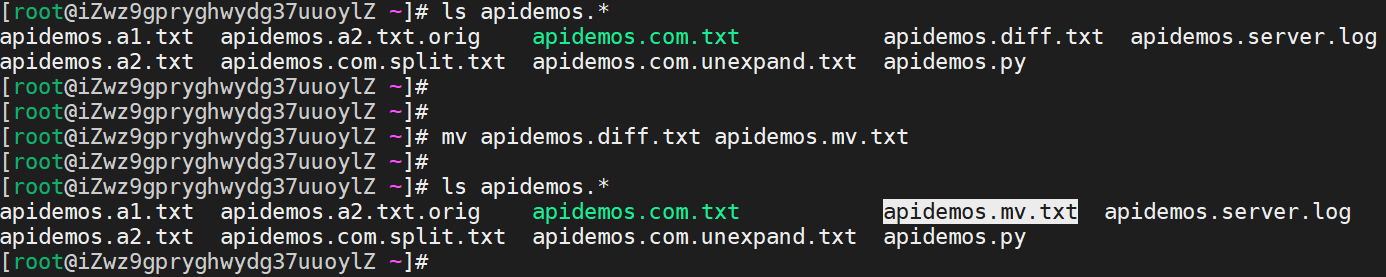
Change the name of the directory /root/pic to /root/mypic
[root@rhel ~]# mv /root/pic /root/mypicMove all files in the directory /usr/men to the current directory (denoted by . ) into the current directory
mv /usr/men/* .Moving files
mv file_1.txt /home/office/Moving multiple files
mv file_2.txt file_3.txt file_4.txt /home/office/
mv *.txt /home/office/Mobile Directory
mv directory_1/ /home/office/Rename a file or directory
mv file_1.txt file_2.txt # Rename the file file_1.txt to file_2.txtRename Directory
mv directory_1/ directory_2/Print mobile information
mv -v *.txt /home/officePrompt for overwritten files
mv -i file_1.txt /home/officeUpdate only when the source file is newer than the target file
mv -uv *.txt /home/officeDo not overwrite any existing files
mv -vn *.txt /home/officeCreate backups during replication
mv -bv *.txt /home/officeUnconditionally overwrite existing files
mv -f *.txt /home/office ApiDemos™
ApiDemos™