How to Compare Strings in Python

Introduction
When working with strings in Python, it is often necessary to compare them to check for equality, find similarities, or sort them in a certain order. Python provides various methods for comparing strings, offering flexibility and convenience to handle string comparisons.
In this article, we will explore different techniques to compare strings in Python programming. We will cover basic comparison operators, case-sensitive and case-insensitive comparisons, string methods, regular expressions, and advanced comparison techniques. So, let’s dive in!
Basic Comparison Operators
Python provides a set of comparison operators that can be used to compare two strings based on their lexical order. These operators include:
==(equal to) – checks if two strings are exactly the same!=(not equal to) – checks if two strings are not the same<(less than) – checks if the first string is less than the second one>(greater than) – checks if the first string is greater than the second one<=(less than or equal to) – checks if the first string is less than or equal to the second one>=(greater than or equal to) – checks if the first string is greater than or equal to the second one
Let’s see some examples to understand how these operators work:
string1 = "apple"
string2 = "banana"
string3 = "apple"
print(string1 == string2) # False
print(string1 != string2) # True
print(string1 < string2) # True
print(string1 <= string3) # True
print(string1 > string3) # False
print(string2 >= string3) # True
Output:
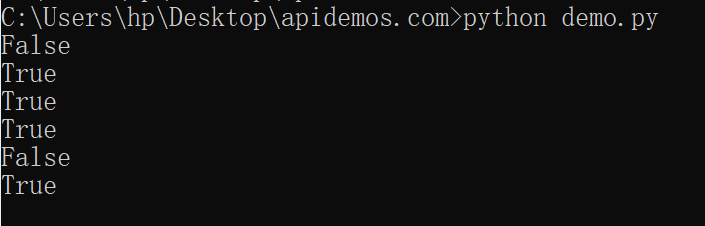
The above code compares three strings: string1, string2, and string3. As a result, we get boolean values (True or False) indicating the comparison result.
Case-Sensitive and Case-Insensitive Comparisons
By default, Python performs case-sensitive comparisons. It means that uppercase and lowercase letters are considered distinct. For example, “apple” and “Apple” are two different strings when compared using basic comparison operators.
If you want to perform case-insensitive comparisons, there are a couple of approaches you can use. One way is to convert both strings to either lowercase or uppercase before comparing them. Let’s see an example:
string1 = "apple"
string2 = "Apple"
print(string1 == string2) # False (case-sensitive)
print(string1.lower() == string2.lower()) # True (case-insensitive)
print(string1.upper() == string2.upper()) # True (case-insensitive)
Output:
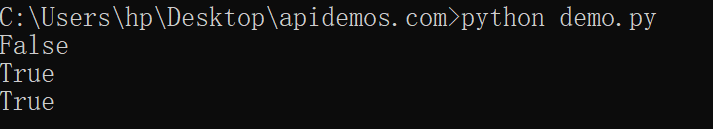
In the above code, we compare string1 and string2 using the lower() and upper() methods, respectively, which convert the strings into lowercase and uppercase. As a result, we get a case-insensitive comparison.
Another approach is to use the casefold() method, which performs a case-insensitive comparison regardless of the current locale. Let’s see an example:
string1 = "apple"
string2 = "Apple"
print(string1 == string2) # False (case-sensitive)
print(string1.casefold() == string2.casefold()) # True (case-insensitive)
Output:

Here, we compare string1 and string2 after applying the casefold() method, resulting in a case-insensitive comparison.
String Methods for Comparison
Python provides several built-in string methods that are helpful for string comparison. These methods can be used to check if a string starts with or ends with another string, or to find a substring within a string. Some commonly used methods include:
startswith()– checks if a string starts with a specified substringendswith()– checks if a string ends with a specified substringfind()– finds the first occurrence of a substring within a stringcount()– counts the number of non-overlapping occurrences of a substring within a string
Let’s understand these methods with some examples:
string = "Hello, world!"
print(string.startswith("Hello")) # True
print(string.endswith("world!")) # True
print(string.find("world")) # 7
print(string.count("o")) # 2
Output:
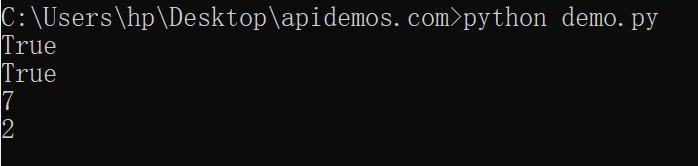
In the above code, we use the startswith() method to check if the string starts with “Hello”, the endswith() method to check if it ends with “world!”, the find() method to find the index of the first occurrence of “world” in the string, and the count() method to count the number of occurrences of the letter “o” in the string.
These methods can be used creatively to compare strings based on specific requirements.
Regular Expressions for Comparison
Regular expressions (regex) provide a powerful and flexible way to compare and manipulate strings. Python’s re module allows us to utilize regular expressions for string comparison.
Here are some useful regex functions provided by the re module for string comparison:
match()– checks if the regex pattern matches at the beginning of the stringsearch()– checks if the regex pattern matches anywhere in the stringfindall()– finds all occurrences of the regex pattern in the stringfinditer()– returns an iterator yielding match objects for all occurrences of the regex pattern in the string
Let’s look at an example to see how regular expressions can be used for string comparison:
import re
string = "abc123def456"
pattern = r"\d+"
print(re.match(pattern, string)) # None (does not match at beginning)
print(re.search(pattern, string)) # <re.Match object; span=(3, 6), match='123'>
print(re.findall(pattern, string)) # ['123', '456']
print([match.group() for match in re.finditer(pattern, string)]) # ['123', '456']
Output:

In the above code, we define a regex pattern \d+ to match one or more digits. We then use various re methods to perform string comparisons. The match() method checks if the pattern matches at the beginning, the search() method checks if it matches anywhere in the string, the findall() method finds all occurrences of the pattern, and the finditer() method returns an iterator of match objects.
Advanced Comparison Techniques
In addition to the previously mentioned methods, Python provides some advanced comparison techniques that can be useful in specific cases.
Levenshtein Distance
The Levenshtein distance, also known as the edit distance, measures the minimum number of single-character edits (insertions, deletions, or substitutions) required to change one string into another. Python’s python-Levenshtein library offers an efficient way to calculate this distance.
To use the python-Levenshtein library, you need to install it first by running the following command:
pip install python-Levenshtein
Here’s an example that demonstrates the calculation of the Levenshtein distance:
import Levenshtein
string1 = "kitten"
string2 = "sitting"
distance = Levenshtein.distance(string1, string2)
print(distance) # 3
In the above code, we import the Levenshtein module and use the distance() function to calculate the Levenshtein distance between string1 and string2. The result is printed, which shows that it takes 3 edits to change “kitten” into “sitting”.
Fuzzy Matching
Fuzzy matching refers to the process of finding strings that are approximately equal or similar to a given pattern. Python provides various libraries, such as fuzzywuzzy and difflib, to perform fuzzy matching.
To use the fuzzywuzzy library, you need to install it first by running the following command:
pip install fuzzywuzzy
Here’s an example that demonstrates fuzzy matching using fuzzywuzzy:
from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz
string1 = "apple"
string2 = "aple"
similarity_ratio = fuzz.ratio(string1, string2)
print(similarity_ratio) # 91
In the above code, we import the fuzz module from fuzzywuzzy and use the ratio() function to calculate the similarity ratio between string1 and string2. The result is printedas 91, indicating a high degree of similarity between the two strings.
The difflib library is another option for fuzzy matching in Python. It provides classes and functions to compare sequences and generate differences between them. Here’s an example:
import difflib
string1 = "apple"
string2 = "aple"
matcher = difflib.SequenceMatcher(None, string1, string2)
similarity_ratio = matcher.ratio()
print(similarity_ratio) # 0.8
In the above code, we create a SequenceMatcher object by passing None as the first argument (which indicates the default behavior), and the two strings string1 and string2. We then use the ratio() method to calculate the similarity ratio. The result is printed as 0.8, indicating an 80% similarity between the two strings.
These advanced techniques provide more flexibility when it comes to comparing strings that are not an exact match and can be handy in fuzzy matching scenarios.
Conclusion
Comparing strings is a common task in Python programming, and it can involve various considerations such as case sensitivity, substring matching, and fuzzy matching. In this article, we explored different techniques for comparing strings in Python, including basic comparison operators, case-sensitive and case-insensitive comparisons, string methods, regular expressions, Levenshtein distance calculation, and fuzzy matching.
By understanding and applying these techniques, you can effectively compare strings in Python and handle a wide range of string comparison tasks in your programs. Remember to consider the requirements of your specific use case and choose the most appropriate comparison technique accordingly.
 ApiDemos™
ApiDemos™